E-commerce, or electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It encompasses a range of online activities that enable businesses and consumers to conduct transactions without the need for physical stores or face-to-face interactions. E-commerce can include various models and technologies designed to facilitate online transactions and interactions.
Key Components of E-Commerce
- Types of E-Commerce Models:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers. Examples include online retailers like Amazon or clothing brands selling directly to customers.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Transactions between businesses. This model is common in wholesale trade and supplier relationships.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by third-party platforms like eBay or Craigslist.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): Individuals sell products or offer services to businesses. Examples include freelance platforms like Upwork or content creation services.
- Key E-Commerce Components:
- Online Stores and Marketplaces: Platforms where goods and services are listed for sale. This includes standalone websites and large online marketplaces like eBay and Etsy.
- Payment Gateways: Systems that handle online payments securely, such as PayPal, Stripe, or traditional credit card processing systems.
- Shopping Carts: Software that allows customers to select and manage items they wish to purchase before proceeding to checkout.
- Product Catalogs: Organized listings of products or services, often with detailed descriptions, images, and pricing information.
- Customer Service: Support provided to assist customers with their purchases, address issues, and handle inquiries. This can include chat support, email, and phone support.
- E-Commerce Technologies:
- Websites and Mobile Apps: Platforms for displaying products, processing transactions, and interacting with customers.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Tools for managing and updating the content on e-commerce sites, such as Shopify or WooCommerce.
- Data Analytics: Tools and techniques for analyzing customer behavior, sales trends, and other metrics to optimize e-commerce strategies.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Techniques used to improve the visibility of e-commerce sites in search engine results.
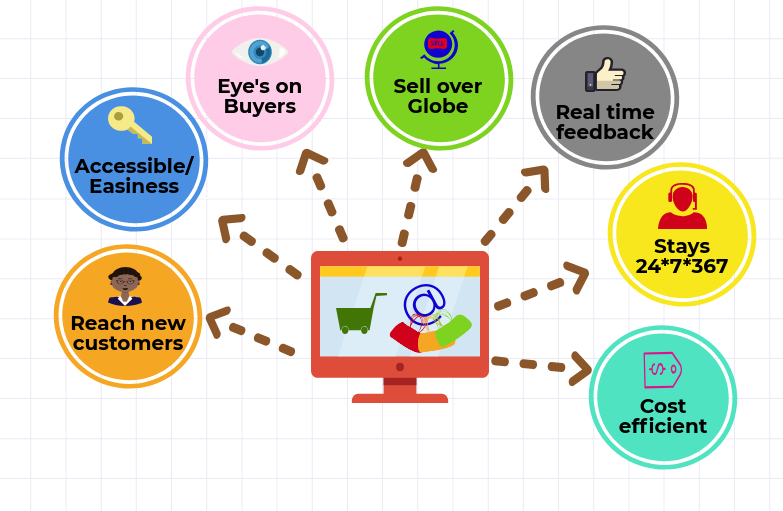
- Benefits of E-Commerce:
- Global Reach: Enables businesses to reach customers around the world without physical store limitations.
- Convenience: Allows customers to shop anytime and anywhere, improving accessibility and convenience.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for physical storefronts and related overhead costs.
- Personalization: Utilizes data to offer personalized shopping experiences and targeted marketing.
- Challenges in E-Commerce:
- Security and Privacy: Ensuring that customer data and transactions are secure from cyber threats and breaches.
- Competition: The online marketplace is highly competitive, requiring businesses to differentiate themselves and optimize their offerings.
- Logistics and Fulfillment: Managing inventory, shipping, and returns can be complex, especially for businesses with a global customer base.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal requirements, including data protection laws and tax regulations, which can vary by region.